Feature Publication Archive
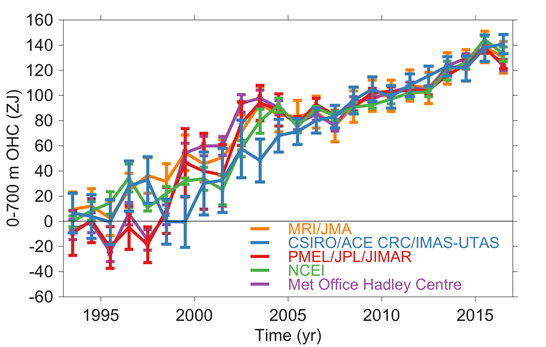
Time series of annual average global integrals of in situ estimates of upper (0–700 m) OHCA (1 ZJ = 10²¹ Joules) for 1993–2016 with standard errors of the mean.
Johnson, G.C. (2017): Overview. In State of the Climate in 2016, Global Oceans. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc., 98 (8), S63
Johnson, G.C., J.M. Lyman, T. Boyer, C.M. Domingues, J. Gilson, M. Ishii, R. Killick, D. Monselan, and S. Wijffels (2017): Ocean heat content. In State of the Climate in 2016, Global Oceans. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc., 98 (8), S66–S69
Johnson, G.C., J. Reagan, J.M. Lyman, T. Boyer, C. Schmid, and R. Locarnini (2017): Salinity. In State of the Climate in 2016, Global Oceans. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc., 98 (8), S69–S75
Feely, R.A., R. Wanninkhof, P. Landschützer, B.R. Carter, and J.A. Triñanes (2017): Ocean carbon. In State of the Climate in 2016, Global Oceans. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc., 98 (8), S89–S92.
Overland, J., E. Hanna, I. Hanssen-Bauer, S.-J. Kim, J.E. Walsh, M. Wang, U.S. Bhatt, and R.L. Thoman (2017): Arctic air temperature. In State of the Climate in 2016, The Arctic. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc., 98 (8), S130–S131.
NOAA has led, for 27 years, a team of international scientists in issuing annual reports on the state of the climate focusing on the year just passed. The State of the Climate in 2016 report, published as a supplement to Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society in August 2017, is the most recent release of this report. Seven Federal, JISAO (Joint Institute for the Study of the Atmosphere and Ocean, University of Washington), and JIMAR (Joint Institute for Marine and Atmospheric Research, University of Hawaii) scientists resident at PMEL co-authored four of twelve sections in the... more »
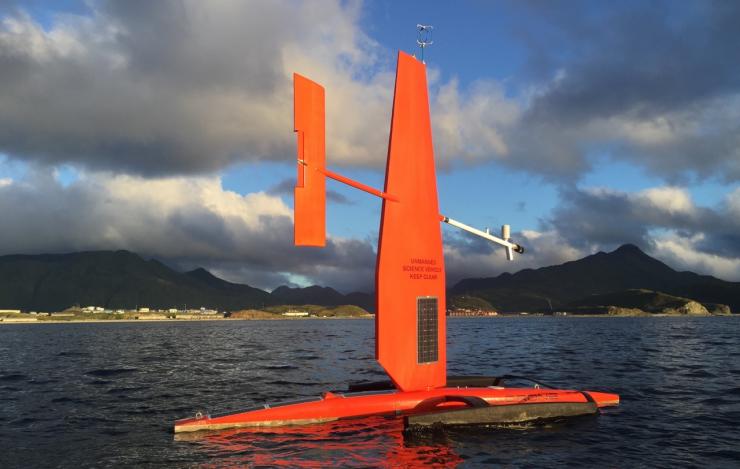

A Saildrone departs Dutch Harbor, AK in 2016 on it's way to test sensors on this platform for multi-disciplinary science
Mordy, C.W., E. Cokelet, A. DeRobertis, R. Jenkins, C. Meinig, C. Berchok, J. Crance, J. Cross, C. Kuhn, N. Lawrence-Slavas, P. Stabeno, J. Sterling, H. Tabisola, and I. Wangen (2017): Advances in ecosystem research: Saildrone surveys of oceanography, fish and marine mammals in the Bering Sea. Oceanography, 30, 2, doi:10.5670/oceanog.2017.230.
This month's featured article provides an overview of the first Saildrone mission conducted jointly between NOAA Fisheries Alaska Fisheries Science Center (AFSC) and Pacific Marine Environmental Laboratory (PMEL).
The Saildrone is an autonomous surface vehicle outfitted with meteorological and oceanographic sensors, including passive and active acoustics. In 2016, NOAA used the Saildrone to survey the Bering Sea, a region known for its harsh conditions (e.g., storms, low light, biofouling) and high level of biological productivity. The mission was a success, and the Saildrone proved... more »
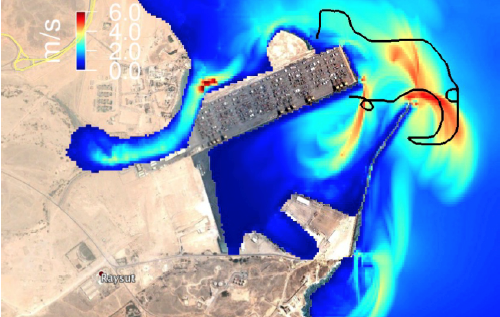
Maersk Mandraki breaks moorings during the 2004 Sumatra Tsunami. The 285-m container ship was pulled out of the Port of Salalah, Oman, drifted around the breakwater, and nearly struck the breakwater on the ocean side (Image courtesy of Jose Borrero).
Lynett, P.J., K. Gately, R. Wilson, L. Montoya, D. Arcas, B. Aytore, Y. Bai, J.D. Bricker, M.J. Castro, K.F. Cheung, C.G. David, G.G. Doğan, C. Escalante, J.M. González-Vida, S.T. Grilli, T.W. Heitmann, J.J. Horrillo, U. Kânoglu, R. Kian, J.T. Kirby, W. Li, J. Macías, D.J. Nicolsky, S. Ortega, A. Pampell-Manis, Y.S. Park, V. Roeber, N. Sharghivand, M. Shelby, F. Shi, B. Tehranirad, E. Tolkova, H.K. Thio, D. Velioğlu, A.C. Yalçiner, Y. Yamazaki, A. Zaytsev, and Y..J. Zhang (2017): Inter-model analysis of tsunami-induced coastal currents. Ocean Model., 114, 14–32, doi:10.1016/j.ocemod.2017.04.003.
Over the last decade, a number of tsunami events originating from distant regions of the Pacific Ocean have impacted the US West Coast. In some cases, the arrival of tsunami waves associated with these events has coincided with low tide levels, such as the 2006 Kuril Islands (Russia) and 2011 Tohoku (Japan) events. This fortunate circumstance helped minimize inundation of dry land, but also illustrated that tsunami-induced water currents can result in severe damage to harbor facilities, moored vessels, and the waterfront infrastructure, in general.
Traditionally, the validation of... more »
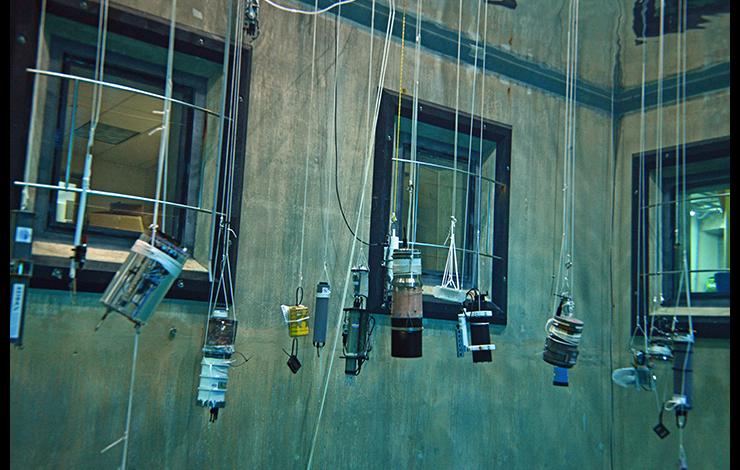

Deployment of pH sensors in the Monterey Bay Aquarium Research Institute's test pool during an early phase of the Wendy Schmidt Ocean Health XPRIZE competition.
Okazaki, R.R., A.J. Sutton, S.R. Alin, R.A. Feely, A.G. Dickson, C.L. Sabine, P.M.E. Bunje, and J.I. Virmani (2017): Evaluation of marine pH sensors under controlled and natural conditions for the Wendy Schmidt Ocean Health XPRIZE. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods, doi:10.1002/lom3.10189.
Since the beginning of the Industrial Revolution, human activity has increased levels of carbon dioxide (CO2) released into the Earth’s atmosphere, with nearly 30% of that CO2 being absorbed by the oceans. Decades of observations have shown that the ocean’s absorption of CO2 results in a decline in seawater pH levels, thus changing the overall chemical composition of the ocean. This process, known as ocean acidification (OA), is occurring faster now than at any other time in the geologic record.
There is an ever-increasing body of documentation of OA... more »

Hydrophone and mooring being deployed using crane from U.S. Coast Guard ship Sequoia. Crane block can be seen at top of image, as floats are being lowered into water.
Dziak, R.P., J.H. Haxel, H. Matsumoto, T.-K. Lau, S. Heimlich, S. Nieukirk, D.K. Mellinger, J. Osse, C. Meinig, N. Delich, and S. Stalin (2017): Ambient sound at Challenger Deep, Mariana Trench.Oceanography, 30 (2), doi:10.5670/oceanog.2017.240.
You might imagine the bottom of the ocean’s deepest point, seven miles down, to be a very quiet place. However, NOAA and partner scientists, making the first recordings from the Challenger Deep trough in the Mariana Trench in the Pacific Ocean, found something remarkably different: a wide variety of human-caused and natural sounds, including the hum of ship propellers, active sonar, earthquakes, baleen whales, and a category 4 typhoon passing near the sensor.
Human-generated noise has increased steadily over the past several decades. This project, which was funded by the NOAA Office... more »


