Glossary and Acronyms
Go to: A - B - C - D - E - F - G - H - I - J - K - L - M - N - O - P - Q - R - S - T - U - V - W - X - Y - Z
ADCP - Acoustic Doppler Current Profiles. An instrument that measures ocean currents based on doppler shifts in backscattered acoustic signals
AIRT - Air temperature, measured by the TAO buoys three meters above the sea surface.
Anomaly - Difference between data and a climatology.
BPor SLP- Atmospheric barometric pressure measured at three m above the ocean surface
Climatology - Average conditions based on historical data. Seasonal climatologies represent best estimate of average conditions for each month (January through December).
Current - Horizontal velocity of ocean flow.
Data averaging intervals - Instruments sample the environment at various time intervals or during various time intervals, such as one hour, or 1 day (see TAO Data Sampling Regimes). Later, the data are averaged over a longer time period, such as five days or a month.
- Monthly - Average of daily data collected during each month.
- 5-Day - Average of daily data collected during consecutive five day intervals, and subsequently smoothed with a 1-2-1 filter.
- Daily - Average of highest resolution data collected each day.
DYN - Dynamic Height. This is a measure of the elevation of the sea level , calculated by integrating the specific volume anomaly of the sea water between the sea surface and 500 m depth.
D(z) - Subsurface density (sigma-theta).
EQ or EQUA identifies data at the Equator.
FD Cur - Ocean currents measured at fixed depths
Heat - Heat content of the upper layers of the ocean, from the surface to 300 meters.
Isotherms - Surfaces of constant temperature within the ocean, or lines of constant temperature on a time-depth plot, a depth-longitude plot, or a latitude depth plot
LWR or LW Rad - Incoming longwave radiation measured at three m above the ocean surface
Ocean Derived - Data computed from ocean sensor data, such as heat content, dynamic height, 20°C isotherm depth, and transports.
RH - Relative Humidity, measured by the TAO buoys three meters above the sea surface.
Sampling - Temporal and spatial resolution of data.
Sea T(z) - Subsurface sea temperatures.
Sigma-Theta - Conductivity and temperature are first used to compute salinity, which is then combined with potential temperature to compute the potential density anomaly (sigma-theta) defined as
sigma-theta = 1/V(S,Theta,P) - 1000 kg m s-3
where V is specific volume, S is salinity, Theta is potental temperature, and P is set to zero. The algorithm used is from "Algorithms for computation of fundamental properties of seawater" by Fofonoff and Millard (UNESCO Technical Papers in Marine Science, 44, 1983).
SLP or BP - Atmospheric barometric pressure measured at three m above the ocean surface.
SOI - Southern Oscillation Index - is a widely used scale based on the surface (atmospheric) pressure difference between Tahiti and Darwin, Australia. It is highly correlated with tropical sea surface temperature anomaly indices such as Nino3.
SSD - Sea surface density (sigma-theta) at one meter depth.
SSS - Sea surface salinity at one meter depth.
SST - Sea surface temperature, measured by the TAO buoys at one meter below the surface.
Surface Met - Meteorological data from the sea surface including SST, AIRT, winds, RH, precipitation and shortwave radiation. Standard surface meteorological data include SST AIRT, winds and RH.
SWR or SW Rad- Incoming shortwave radiation measured at three m above the ocean surface.
S(z) Subsurface salinity.
TAO - Tropical Atmosphere Ocean (TAO) Array
TRITON - TRIangle Trans-Ocean buoy Network, maintained by JAMSTEC in collaboration with TAO.
Transport - Volume of ocean water moving through an imaginary surface per second. Often computed as a transport per unit width from a single buoy by integrating the ocean currents over a range of depth in the upper ocean. Transport units are Sverdrup ( 1 Sverdrup= 10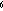 m
m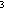 /s)
/s)
TZ-AVE - Depth Averaged Temperature, measured by the TAO buoys from the surface to 300m depth.
T1, T2, ...., T10 - Subsurface temperatures, measured by the TAO buoys. Standard instrument depths for ATLAS sites are listed below:
| DEPTHS (m) | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 | T6 | T7 | T8 | T9 | T10 |
| East of 155°W | 20 | 40 | 60 | 80 | 100 | 120 | 140 | 180 | 300 | 500 |
| 155°W and west | 25 | 50 | 75 | 100 | 125 | 150 | 200 | 250 | 300 | 500 |
Instrument depths for current-meter sites on the equator at 156°E, 165°E, 140°W, 110°W,are different from the above, and have varied over time. For graphical info on instrument depths, see the TAO data availability page. In NetCDF files used for web displays, temperatures have been regridded to the above standard depths.
UWND - TAO buoys measure the wind speed and direction four meters above the sea surface. UWND is the East-West component, also referred to as the U or zonal component of the wind. If it is positive, the East-West component of the wind is blowing towards the East. If it is negative, this component is blowing towards the West.
VWND - TAO buoys measure the wind speed and direction four meters above the sea surface. VWND is the North-South component of the wind, also referred to as the V or meridional component of the wind. If it is positive, the North-South component of the wind is blowing towards the North. If it is negative, this component is blowing towards the South.
Wind - Vectors showing the speed and direction of winds at four meters above the sea surface, measured by the TAO buoys. The arrow head shows the direction the wind is blowing towards, and the length of the vector indicates the strength of the wind speed.
Wnd Vec - Wind vectors (see "wind", above).
WSPD - Scalar wind speed computed from hourly or daily data using the relation wspd = sqrt(uwnd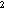 + vwnd
+ vwnd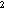 ).
).
WDIR - Wind Direction in degrees clockwise from North computed from hourly or daily data using the relation wdir = (180 / 3.14) * arctan(uwnd / vwnd)
Z20 or 20C Dep - Depth at which ocean temperature is twenty degrees Celsius.


